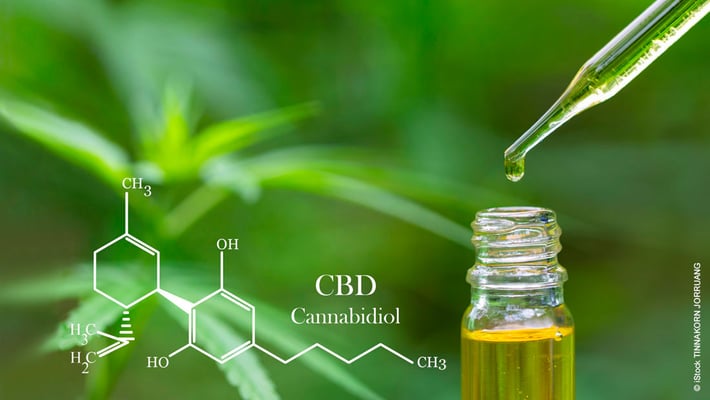
Cannabidiol, or CBD for short, is an extract of the female hemp plant that has recently become freely available in the EU. Unlike THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), it is not psychoactive and therefore does not have an intoxicating effect. Rather, the molecule is said to have anticonvulsant and anti-inflammatory effects. We asked ourselves, “How are these natural substances extracted?” Read more about CBD production here.
Where does the trend for CBD production come from?
The trend for CBD comes from the USA, where CBD is used as supplement in food and beverages, though without the official consent of the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration). The exploitation of cannabidiol went hand in hand with a liberalisation of the cultivation and processing of hemp for medicinal purposes. Where CBD is a by-product of the extraction of the psychoactive ingredient THC. However, there is now also targeted extraction of CBD from hemp that contains little to no THC, as demand has increased very strongly.
In the EU, however, CBD actually falls under the term "novel food" and is therefore more of a lifestyle product or food supplement. This means that no medical effect may be advertised.
How is CBD oil made from the hemp plant? What are the typical methods for extracting CBD?
How are such natural substances actually extracted? At the beginning, the base material is harvested, dried and processed. After that, the plant parts are ground or chopped. In the case of cannabidiol or THC, the material must also be heated briefly and strongly so that the active substances are formed.
Different CBD production processes:
1. CBD extraction with hydrocarbons
Extraction with hydrocarbons such as n-heptane is one of the most common methods. Since the natural substance CBD is not very soluble in water, paraffinic solvents are a good choice. In a specialised apparatus, the plant material is repeatedly flushed with fresh solvent until it is exhausted. The n-heptane is eventually removed by distillation and the last traces of it are removed under reduced pressure. The procedure is well known and can be easily carried out.
2. Supercritical carbon dioxide for CBD extraction
Under pressure carbon dioxide is a colourless liquid. If you heat this under pressure, it becomes supercritical and behaves like both a gas and a liquid. In this state, it easily penetrates the dried hemp and dissolves the active substances it contains. Subsequently the carbon dioxide and solid plant material are separated and the carbon dioxide is allowed to evaporate. The technical complexity of this process is very high. This same process is used to extract caffeine from coffee beans.
3. Alcohols and vegetable oils for CBD extraction
Alcohols such as ethanol and methanol can be used for extraction in the same way as n-heptane or other paraffinic solvents. However, since they have different solvent properties, they do not extract exactly the same substances from the hemp. With the right choice of solvent, one can therefore positively influence the result. Alternatively, one can soak the hemp in vegetable oil and thus produce a direct extract.
Stay informed with our Blog!Subscribe to our blog free of charge and benefit from regular information on sustainability, chemical purchasing, research & development and supply chain management: |
Further steps in the CBD process
In all above mentioned CBD extraction cases, you get a crude extract that contains cannabidiol as well as other natural substances, THC, waxes and vegetable fats and oils. These have to be separated from each other. In the processing of such mixtures (very similar to the processing of active pharmaceutical substances, API), paraffinic hydrocarbons are often used. They are used in processes such as crystallisation, chromatography or for washing the finished substance. Particularly suitable are n-pentane, n-heptane, n-octane or iso-octane due to their physical properties (e.g. boiling point, solubility).
The purified CBD can now be further processed, usually dissolved in a neutral vegetable oil. The carrier oil increases the bioavailability of the cannabidiol in the human body. This oil is offered for external and internal applications. However, other uses are also conceivable, for example in cosmetics, drinks, cereal bars, food supplements, sweets or liquids for e-cigarettes.
This might also be of interest to you:
- Quality control in CBD production
- How to make the right choice when buying solvents for the pharmaceutical industry!
Conclusion
In order to extract CBD from the hemp plant, there are various extraction methods. One of the most common methods is extraction with hydrocarbons such as n-heptane, due to their advantageous physical properties. After processing the crude extract, the purified CBD is further processed and, in most cases, dissolved in a neutral vegetable oil, before being used in external and internal applications.
This blog has been posted first on Jan 29, 2021 and has been updated Jan 5, 2024.